The Hao AI Lab analysis staff on the College of California San Diego — on the forefront of pioneering AI mannequin innovation — lately obtained an NVIDIA DGX B200 system to raise their vital work in massive language mannequin inference.
Many LLM inference platforms in manufacturing at this time, resembling NVIDIA Dynamo, use analysis ideas that originated within the Hao AI Lab, together with DistServe.
How Is Hao AI Lab Utilizing the DGX B200?
With the DGX B200 now totally accessible to the Hao AI Lab and broader UC San Diego group on the College of Computing, Info and Knowledge Sciences’ San Diego Supercomputer Heart, the analysis alternatives are boundless.
“DGX B200 is likely one of the strongest AI programs from NVIDIA thus far, which implies that its efficiency is among the many greatest on this planet,” mentioned Hao Zhang, assistant professor within the Halıcıoğlu Knowledge Science Institute and division of laptop science and engineering at UC San Diego. “It permits us to prototype and experiment a lot quicker than utilizing previous-generation {hardware}.”
Two Hao AI Lab tasks the DGX B200 is accelerating are FastVideo and the Lmgame benchmark.
FastVideo focuses on coaching a household of video technology fashions to supply a five-second video based mostly on a given textual content immediate — in simply 5 seconds.
The analysis part of FastVideo faucets into NVIDIA H200 GPUs along with the DGX B200 system.
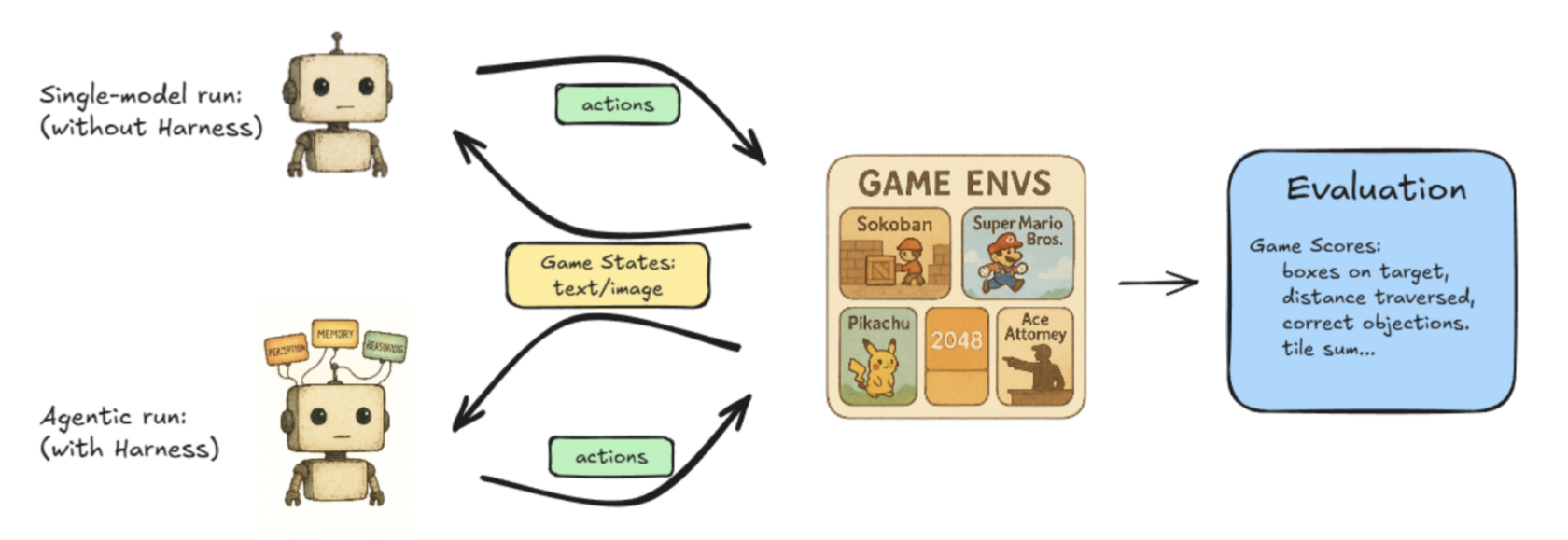
Lmgame-bench is a benchmarking suite that places LLMs to the take a look at utilizing common on-line video games together with Tetris and Tremendous Mario Bros. Customers can take a look at one mannequin at a time or put two fashions up in opposition to one another to measure their efficiency.
Different ongoing tasks at Hao AI Labs discover new methods to realize low-latency LLM serving, pushing massive language fashions towards real-time responsiveness.
“Our present analysis makes use of the DGX B200 to discover the subsequent frontier of low-latency LLM-serving on the superior {hardware} specs the system provides us,” mentioned Junda Chen, a doctoral candidate in laptop science at UC San Diego.
How DistServe Influenced Disaggregated Serving
Disaggregated inference is a manner to make sure large-scale LLM-serving engines can obtain the optimum mixture system throughput whereas sustaining acceptably low latency for person requests.
The advantage of disaggregated inference lies in optimizing what DistServe calls “goodput” as a substitute of “throughput” within the LLM-serving engine.
Right here’s the distinction:
Throughput is measured by the variety of tokens per second that your entire system can generate. Increased throughput means decrease price to generate every token to serve the person. For a very long time, throughput was the one metric utilized by LLM-serving engines to measure their efficiency in opposition to each other.
Whereas throughput measures the mixture efficiency of the system, it doesn’t straight correlate to the latency {that a} person perceives. If a person calls for decrease latency to generate the tokens, the system has to sacrifice throughput.
This pure trade-off between throughput and latency is what led the DistServe staff to suggest a brand new metric, “goodput”: the measure of throughput whereas satisfying the user-specified latency aims, often known as service-level aims. In different phrases, goodput represents the general well being of a system whereas satisfying person expertise.
DistServe reveals that goodput is a significantly better metric for LLM-serving programs, because it components in each price and repair high quality. Goodput results in optimum effectivity and ultimate output from a mannequin.
How Can Builders Obtain Optimum Goodput?
When a person makes a request in an LLM system, the system takes the person enter and generates the primary token, referred to as prefill. Then, the system creates quite a few output tokens, one after one other, predicting every token’s future conduct based mostly on previous requests’ outcomes. This course of is named decode.
Prefill and decode have traditionally run on the identical GPU, however the researchers behind DistServe discovered that splitting them onto completely different GPUs maximizes goodput.
“Beforehand, in case you put these two jobs on a GPU, they’d compete with one another for sources, which might make it sluggish from a person perspective,” Chen mentioned. “Now, if I cut up the roles onto two completely different units of GPUs — one doing prefill, which is compute intensive, and the opposite doing decode, which is extra reminiscence intensive — we are able to basically get rid of the interference between the 2 jobs, making each jobs run quicker.
This course of known as prefill/decode disaggregation, or separating the prefill from decode to get better goodput.
Growing goodput and utilizing the disaggregated inference technique permits the continual scaling of workloads with out compromising on low-latency or high-quality mannequin responses.
NVIDIA Dynamo — an open-source framework designed to speed up and scale generative AI fashions on the highest effectivity ranges with the bottom price — permits scaling disaggregated inference.
Along with these tasks, cross-departmental collaborations, resembling in healthcare and biology, are underway at UC San Diego to additional optimize an array of analysis tasks utilizing the NVIDIA DGX B200, as researchers proceed exploring how AI platforms can speed up innovation.
Study extra in regards to the NVIDIA DGX B200 system.